Chapter 3: Using Java on Your Pages
![]()
|
<HTML>
<HEAD> <TITLE>Hey, it's Java<TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY BGCOLOR=WHITE> <APPLET CODEBASE="classes" -> CODE="HelloWorld.class" WIDTH=200 HEIGHT=50 -> ALIGN=RIGHT> </APPLET> </BODY> </HTML> |
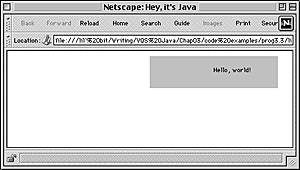
Fig. 3.4 Here the applet is aligned on the right-hand side of the window.
Listing 3.4 Here's another way to move an applet around.
![]()
|
<HTML>
<HEAD> <TITLE>Hey, it's Java<TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY BGCOLOR=WHITE> <APPLET CODEBASE="classes" -> CODE="HelloWorld.class" WIDTH=200 HEIGHT=50 -> HSPACE=100 VSPACE=100> </APPLET> </BODY> </HTML> |
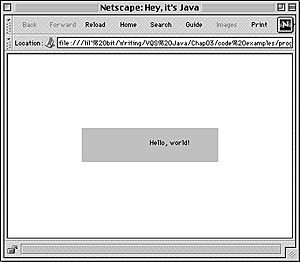
Fig. 3.5 The applet now has a 100-pixel-wide border on every side.
Positioning Java applets on the page
The APPLET tag can be positioned on a Web page much like the IMG tag. Listings 3.3 and 3.4 show how an applet can be moved from the default alignment.
To position a Java applet:
1. <APPLET CODEBASE="classes" CODE="HelloWorld.class" WIDTH=200 HEIGHT=50 ALIGN=RIGHT>
In Figure 3.4, the HelloWorld applet is on the right side of the window. This is because the ALIGN attribute of the APPLET tag has been set to RIGHT.
2. <APPLET CODEBASE="classes" CODE="HelloWorld.class" WIDTH=200 HEIGHT=50 HSPACE=100 VSPACE=100>
In Figure 3.5, the HelloWorld applet is surrounded by 100 pixels of white space on all sides, due to the settings of the HSPACE and VSPACE attributes.
 Tips
Tips
Other valid values for ALIGN are LEFT, RIGHT, TOP, TEXTTOP, MIDDLE, ABSMIDDLE, BASELINE, BOTTOM, and ABSBOTTOM, as described in Table 3.1 (below).
HEIGHT, WIDTH, ALIGN, HSPACE, and VSPACE are all attributes that the APPLET tag shares with the IMG tag. To learn more about these attributes, check out HTML 4 for the World Wide Web, by Elizabeth Castro. (Peachpit Press, 1998)
| Alignment | Meaning |
| LEFT | Aligns the applet area flush left |
| RIGHT | Aligns the applet area flush right |
| TOP | Displays the applet area at the top of the available area |
| TEXTTOP | Aligns the applet area with the highest text displayed adjacent to the applet area |
| MIDDLE | Aligns the middle of the applet area with the baseline of adjacent text |
| ABSMIDDLE | Aligns the middle of the applet area with the middle of the largest adjacent item |
| BASELINE | Aligns the bottom of the applet area with the baseline of adjacent text |
| BOTTOM | Aligns the bottom of the applet area with the bottom of adjacent text |
| ABSBOTTOM | Aligns the bottom of the applet area with the bottom of largest adjacent item |